Introduction
The Gulf Stream, a powerful ocean current that flows along the eastern coast of North America and across the Atlantic Ocean, plays a vital role in regulating the world’s climate and weather patterns. However, climate change is now casting a shadow over this crucial system, with far-reaching consequences for global weather patterns. In this blog post, we will explore how climate change is impacting the Gulf Stream and how these changes are influencing weather events across the world.
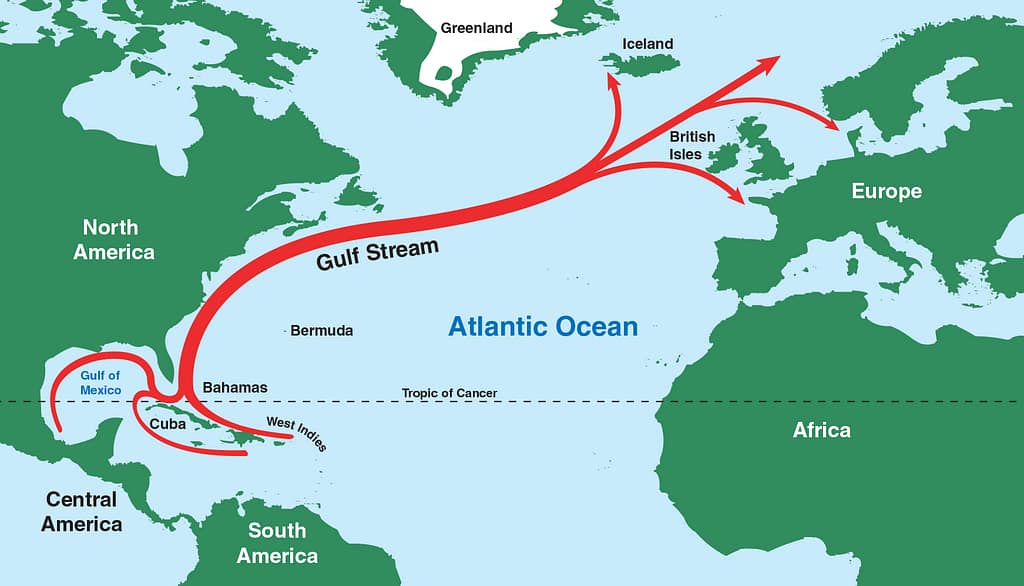
Understanding the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico, flows along the eastern seaboard of the United States, and travels northeastward across the Atlantic Ocean toward Europe. It is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre, a complex system of currents that transports warm water from the tropics toward higher latitudes.
The Gulf Stream plays several critical roles in shaping the world’s climate and weather:
- Heat Transport: The Gulf Stream carries warm water from the equator to higher latitudes, significantly influencing the climate of both North America and Western Europe. This heat transport helps to keep these regions relatively warm compared to other areas at similar latitudes.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The temperature difference between the warm Gulf Stream and the surrounding cooler waters influences atmospheric circulation patterns. This, in turn, affects the positioning of high and low-pressure systems and the development of weather patterns.
- Influence on Weather: The Gulf Stream has a profound impact on weather patterns, including the development of storms, precipitation patterns, and the overall climate of regions bordering the North Atlantic.
Climate Change’s Impact on the Gulf Stream
Climate change, driven by the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, is causing significant changes in the Gulf Stream and its associated weather patterns:
- Weakening Gulf Stream: One of the most concerning effects of climate change on the Gulf Stream is its weakening. As the Arctic warms at an accelerated rate, the temperature difference between the Arctic and the mid-latitudes decreases. This reduces the driving force behind the Gulf Stream, causing it to slow down. A weaker Gulf Stream can disrupt the normal circulation of ocean currents, leading to altered weather patterns.
- Shifted Weather Patterns: The weakening and shifting of the Gulf Stream can lead to changes in weather patterns. For example, Western Europe, which benefits from the warmth brought by the Gulf Stream, may experience cooler and more variable weather if the current weakens significantly.
- More Extreme Weather Events: A weakened Gulf Stream can also lead to more extreme weather events in North America, such as prolonged heatwaves or intense cold snaps. The altered ocean currents can disrupt established weather patterns, leading to more unpredictable and extreme conditions.
- Rising Sea Levels: Climate change is causing sea levels to rise due to the thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of polar ice caps. A weakened Gulf Stream can exacerbate this issue, leading to higher sea levels along the eastern coast of North America and impacting coastal communities.
- Disrupted Ecosystems: Changes in the Gulf Stream can disrupt marine ecosystems, affecting fish populations and migration patterns. This, in turn, can have economic consequences for fishing industries.
- Impact on Hurricanes: The Gulf Stream can influence the development and intensity of hurricanes. Changes in its behavior can affect the paths and strengths of hurricanes, potentially making them more destructive.
Mitigating Climate Change’s Impact on the Gulf Stream
Addressing climate change and its impact on the Gulf Stream is essential for the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants. Here are some steps that can help mitigate these effects:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The primary driver of climate change is the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Reducing emissions through measures such as transitioning to clean energy sources and improving energy efficiency is crucial.
- Conservation and Reforestation: Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems like forests and wetlands can help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change.
- International Cooperation: Climate change is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Nations must work together to reduce emissions and address the broader challenges posed by climate change.
- Adaptive Measures: Communities in vulnerable areas must develop adaptive strategies to cope with changing weather patterns and rising sea levels. This may involve building resilient infrastructure and implementing sustainable land use practices.
- Scientific Research: Continued research into the Gulf Stream and its interactions with climate change is essential for understanding and predicting its behavior accurately. This knowledge can inform mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Conclusion
The Gulf Stream is a critical component of the Earth’s climate system, influencing weather patterns and ecosystems on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Climate change is now altering the behavior of the Gulf Stream, with potentially far-reaching consequences for global weather patterns. It is imperative that we take swift and decisive action to mitigate the effects of climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and protect this vital ocean current. By doing so, we can help safeguard the stability of our planet’s climate and ensure a more predictable and sustainable future for generations to come.

test